Merge Sort
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows:
a. Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each containing 1 element (a list of 1 element is considered sorted).
b. Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
Complexity
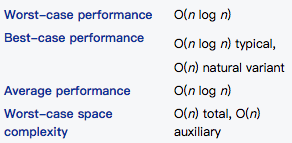
Example
a. Given unsorted list: [6 2 4 1 5 9]
b. Seperate: [2 6] [1 4] [5 9]
c. Merge them: [1 2 4 6] [5 9]
d. Continue merge: [1 2 4 5 6 9]
Implementation in Python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 顾名思意,就是直接从待排序数组里选择一个最小(或最大)的数字,每次都拿一个最小数字出来,
# 顺序放入新数组,直到全部拿完
# 再简单点,对着一群数组说,你们谁最小出列,站到最后边
# 然后继续对剩余的无序数组说,你们谁最小出列,站到最后边
# 再继续刚才的操作,一直到最后一个,继续站到最后边,现在数组有序了,从小到大
import copy
def merge_sort(l):
res = []
if (len(l) <=1): return l
mid = len(l) / 2
left_l = merge_sort(l[: mid])
right_l = merge_sort(l[mid:len(l)])
while (len(left_l)>0 and len(right_l)):
if (left_l[0]>right_l[0]):
res.append(right_l.pop(0))
else:
res.append(left_l.pop(0))
if (len(left_l)>0):
res.extend(merge_sort(left_l))
else:
res.extend(merge_sort(right_l))
return res
def main():
l = [2, 3, 4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 1100, 282828, 1, 20, 0]
li = merge_sort(l)
print li
main()