Quick Sort
Quicksort is a divide and conquer algorithm. Quicksort first divides a large array into two smaller sub-arrays: the low elements and the high elements.
Example
Given a list [6 2 4 1 5 9]
a. pick the first number 6, and compare other numbers with 6, the bigger one is put in the right, otherwise in the lef, so it become: [2 4 1 5 6 9]
b. then quick sort the left part [2 4 1 5] and the right part [9], continue step a, it will become: [1 2 4 5], so the result is [1 2 4 5 6 9]
Complexity
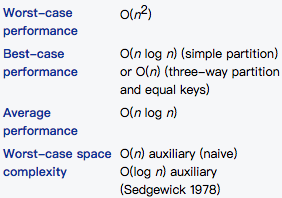
Pseudocode
algorithm quicksort(A, lo, hi) is
if lo < hi then
p := partition(A, lo, hi)
quicksort(A, lo, p – 1)
quicksort(A, p + 1, hi)
algorithm partition(A, lo, hi) is
pivot := A[hi]
i := lo // place for swapping
for j := lo to hi – 1 do
if A[j] ≤ pivot then
swap A[i] with A[j]
i := i + 1
swap A[i] with A[hi]
return i
Implementation in Python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 通过一趟扫描将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,
# 其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,
# 然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,
# 以此达到整个数据变成有序序列
def partition(l, start, end):
middle = l[start]
while (start < end):
while (start<end and l[end] > middle):
end = end-1
l[start] = l[end]
while (start<end and l[start] <= middle):
start = start+1
l[end] = l[start]
l[start] = middle
return start
def quick_sort(l, start, end):
if (start < end):
middle = partition(l, start, end)
quick_sort(l, start, middle-1)
quick_sort(l, middle+1, end)
return l;
def main():
l = [2, 3, 4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 1100, 282828, 1, 20, 0]
li = quick_sort(l, 0, len(l) - 1)
print li
main()