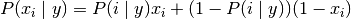- The foundation: Probabilistic model
- Knowledgement and Process
- Constructing a classifier from the probability model
- Parameter estimation and event models
- Codes
- Multinomial Naive Bayes
Naive Bayes Algorithms
The foundation: Probabilistic model
Abstractly, naive Bayes is a conditional probability model: given a problem instance to be classified. Bayes Probability terminology:
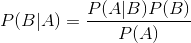
Knowledgement and Process
The sample belongs to the type with the highest probability. The definition is:
a. 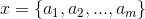 is the features data, a means x’s every feature
is the features data, a means x’s every feature
b. Multiple classes: 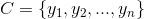
c. Calculate conditional Probabilistic: 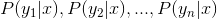
d. If 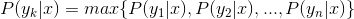 , then
, then 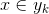
The point is how to calculate the step c:
c.1 Get the training set.
c.2 Calculate the conditional probability:
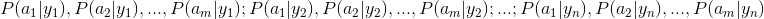
c.3 If features are conditional dependent, based on
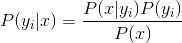
Because the denominator is constant, so maximum the numerator, and features are dependent, so
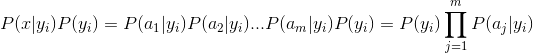
Constructing a classifier from the probability model
The discussion so far has derived the independent feature model, that is, the naive Bayes probability model. The naive Bayes classifier combines this model with a decision rule. One common rule is to pick the hypothesis that is most probable; this is known as the maximum a posteriori or MAP decision rule. The corresponding classifier, a Bayes classifier, is the function that assigns a class label for some k as follows:
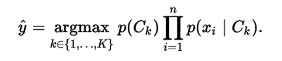
Parameter estimation and event models
- Gaussian Naive Bayes
The likelihood of the features is assumed to be Gaussian:
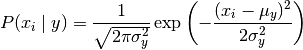
Codes
using scikit-learn package
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
gnb = GaussianNB()
y_pred = gnb.fit(iris.data, iris.target).predict(iris.data)
print("Number of mislabeled points out of a total %d points : %d" % (iris.data.shape[0],(iris.target != y_pred).sum()))
Multinomial Naive Bayes
MultinomialNB implements the naive Bayes algorithm for multinomially distributed data, and is one of the two classic naive Bayes variants used in text classification (where the data are typically represented as word vector counts, although tf-idf vectors are also known to work well in practice).
- Bernoulli Naive Bayes
classification algorithms for data that is distributed according to multivariate Bernoulli distributions; i.e., there may be multiple features but each one is assumed to be a binary-valued (Bernoulli, boolean) variable. Therefore, this class requires samples to be represented as binary-valued feature vectors; if handed any other kind of data, a BernoulliNB instance may binarize its input (depending on the binarize parameter).
The decision rule for Bernoulli naive Bayes is based on