Over-sampling with replacement and has noted that it doesn’t significantly improve minority class recognition. Chawla proposed an over-sampling approach in which the minority class is over-sampled by creating “synthetic” examples rather than by over-sampling with replacement.
They generate synthetic examples in a less application-specific manner, by operating in “feature space” rather than “data space”. The minority class is over-sampled by taking each minority class sample and introducing synthetic examples along the line segments joining any/all of the k minority class nearest neighbors. Depending upon the amount of over-sampling required, neighbors from the k nearest neighbors are randomly chosen.
Its pseudo-code is :

In python package imbalanced-learn, this method can be achieved.
imblearn.over_sampling.SMOTE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
print(__doc__)
sns.set()
# Define some color for the plotting
almost_black = '#262626'
palette = sns.color_palette()
# Generate the dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_classes=2, class_sep=2, weights=[0.1, 0.9],
n_informative=3, n_redundant=1, flip_y=0,
n_features=20, n_clusters_per_class=1,
n_samples=5000, random_state=10)
# Instanciate a PCA object for the sake of easy visualisation
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
# Fit and transform x to visualise inside a 2D feature space
X_vis = pca.fit_transform(X)
# Apply regular SMOTE
sm = SMOTE(kind='regular')
X_resampled, y_resampled = sm.fit_sample(X, y)
X_res_vis = pca.transform(X_resampled)
# Two subplots, unpack the axes array immediately
f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax1.scatter(X_vis[y == 0, 0], X_vis[y == 0, 1], label="Class #0", alpha=0.5,
edgecolor=almost_black, facecolor=palette[0], linewidth=0.15)
ax1.scatter(X_vis[y == 1, 0], X_vis[y == 1, 1], label="Class #1", alpha=0.5,
edgecolor=almost_black, facecolor=palette[2], linewidth=0.15)
ax1.set_title('Original set')
ax2.scatter(X_res_vis[y_resampled == 0, 0], X_res_vis[y_resampled == 0, 1],
label="Class #0", alpha=.5, edgecolor=almost_black,
facecolor=palette[0], linewidth=0.15)
ax2.scatter(X_res_vis[y_resampled == 1, 0], X_res_vis[y_resampled == 1, 1],
label="Class #1", alpha=.5, edgecolor=almost_black,
facecolor=palette[2], linewidth=0.15)
ax2.set_title('SMOTE regular')
plt.show()
The result is:
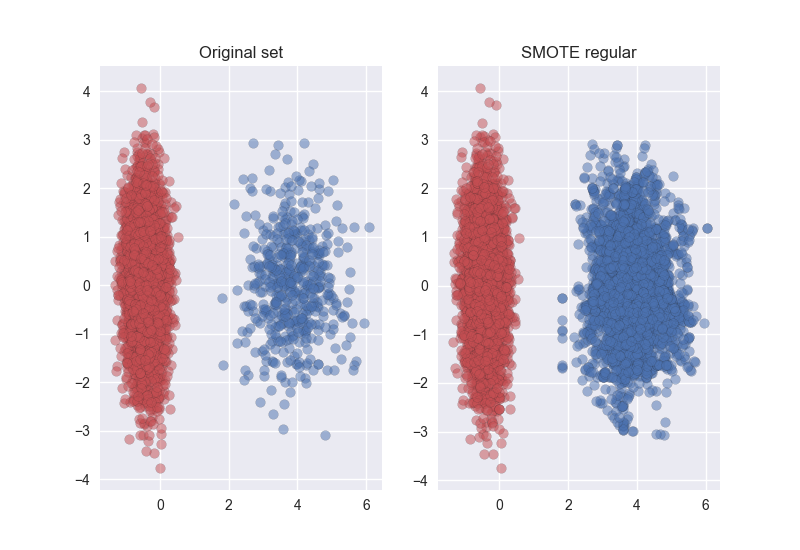
More SMOTE Improvement methods can be got here imblearn.over_sampling.SMOTE
You can get the paper for this method here: SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique